Table of contents
- 在Linux 系统MySQL 安装
- [在Mac 安装MySQL]
- 安装MySQL workbench 及使用
- MySQL 常用的命令
- Head First SQL
在Linux 系统MySQL 安装
在Ubuntu系统下安装MySQL的步骤:
- 更新本地存储库的索引:
sudo apt update - 从APT存储库安装MySQL:
sudo apt install MySQL-server - 查看MySQL版本:
mysql --versin - 安装后,MySQL应已经启动。查看其运行情况:
systemctl status mysql.service
配置MySQL
- 为了提高安全性,
sudo mysql_secure_installation。 关于更改root登陆状态时的验证信息可以参考[] - 按Enter,输入密码
- 一直按
y - 完成设置后,以root身份登陆MySQL。
mysql -u root -pNote::
mysql -h 主机名 -u 用户名 -p-h : 指定客户端所要登录的 MySQL 主机名, 登录本机(localhost 或 127.0.0.1)该参数可以省略; -u : 登录的用户名; -p : 告诉服务器将会使用一个密码来登录, 如果所要登录的用户名密码为空, 可以忽略此选项。 - 推出MySQL ,输入
exit 或者quit关于更改root登陆状态时的验证信息可以参考在Ubuntu中更改MySQL根用户的身份验证方法。更改以后可以直接使用pymsql登陆MySQL进行操作。
[在Mac 安装MySQL]
查看文章
- MySQL 下载安装
首先官方下载安装软件(x86, 64-bit.ARM 不适用)
-
点击安装
-
在用户目录下打开
.zshrc,添加如下命令export PATH=${PATH}:/usr/local/mysql/bin -
在 mac preference 中打开MySQL pannel。点击
Initialize Database,输入相应的密码。 -
在Terminal 端输入
mysql -u root -p,回车后输入第4步的密码。然后进入MySQL
安装MySQL workbench 及使用
- 选择系统及workbench的版本下载
- MySQL to revert back to native password authentication. reference :stack.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'password'; - 连接workbench。
MySQL 常用的命令
MySQL对大小写不敏感,结尾应以;结束。
STATUS;: 显示当前使用的哪个database\c: 在terminal中输入的SQL查询命令过程中,如果想让当前查询命令失效,可以在最后面添加\c,回车即可。show databases;:列出数据库列表use 数据库名;:选择数据库,使用此命令后,后面的命令操作则针对此数据库。show tables: 显示指定的数据库的所有表。show columns from 数据表;:显示数据表的 属性,属性类型,主键信息,是否为NULL,默认值等其他信息。create database 数据库名;:创建新的数据库drop database 数据库名;: 删除数据库create table table_name (column_name column_type);:创建新的表实例如下:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `runoob_tbl` ( `runoob_id` INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT, `runoob_title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, `runoob_author` VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, `submission_date` DATE, PRIMARY KEY ('runooob_id') )ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;- 如果不想字段为 NULL 可以设置为 NOT NULL,如果数据库输入字段为NULL,就会报错。
- AUTO_INCREMENT定义为自增属性,一般用于主键,会自动加1.
- PRIMARY KEY 关键字用于定义列为主键,可以使用多列定义主键,列间以逗号分隔。当然也可以在列名称后面直接加
primary key表示此列为主键。例如runoob_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT - ENGINE设置存储引擎,CHARSET设置编码。
drop table table_name;:删除表insert into table_name (field1, field2, .... fieldN) values (value1,value2,....valueN);: 向表中插入数据。如果数据是字符型,必须使用单引号或者双引号,例如date “2012-12-10”-
清除表信息方式有两种
truncate table table_nameordelete * from table_name,其中truncate 操作中的table可以忽略,delete中的* 可以忽略。trucate速度比delete快,是因为trucate是整体删除,delete是一条条删除,且delete需要写log,而trucate不需要写log。 - 倒出数据库:
mysqldump -u username -p database_name > exporteddb.sql - 倒入数据库:使用MySQL workbench;点击Server -> data import
Head First SQL
The content of this part come from the book Head First SQL
Data and Tables
Data Types
最长用到的data types 有 CHAR, VARCHAR, BLOB, INT, DEC, DATE, and DATETIME.
DECIMAL Data Type
The column definition follows the format DECIMAL(M, D) where M is the maximum number of digits (the precision) and D is the number of digits to the right of the decimal point (the scale).
As an example, if you want a column that accepts values from -9999.99 to 9999.99 the command would be DECIMAL(6,2). As you can see, you still use a precision of 6, but only allow a scale of 2.
Another example is that DECIMAL(6,4). The precision is 6, and scale is 4. such as 12.3456/ 0.1234
M : 是可包含数字的最大数目; D:是小数点后面需要包含的数字。
在官方文件中有如下表述:
M is the maximum number of digits (the precision). It has a range of 1 to 65.
D is the number of digits to the right of the decimal point (the scale). It has a range of 0 to 30 and must be no larger than M.
If D is omitted, the default is 0. If M is omitted, the default is 10.
DESC table_name
使用DESC(DESCRIBE)显示table的基本信息Filed, Type, Null, Key, Default, Extra。
DROP
DROP DATABASE database_name;
DROP TABLE table_name;
INSERT INTO
往table中插入信息
INSERT INTO your_table (column_name1, column_name2,...) VALUES ('value1','value2',...);
关键词:
INSERT INTO,VALUES第一个括号中的是column names, 第二个括号中的是与之相对应的值。各值之间使用,分割。 Any value that goes into a VARCHAR, CHAR, DATE, or BLOB column has single quotes around it. VALUES 括号中的value如果是text,应使用single quotes 结尾使用;
在INSERT INTO statement中,有三种变体:
- 改变column的顺序。此时values 也应该与columns的顺序一致才可以。
- 忽略所有的column的名称。此时values的顺序应该与你建立table时column的顺序是一致的,且应该包括所有的column的值。
- 只填写部分columns。然后在values中也应填写相应部分的值。
在使用INSERT INTO 插入数据时,如果数据是多个,可以一次性在一个INSERT INTO VALUES中全部插入,每一行使用括号括起来,然后使用逗号进行分割
CREATE DATABASE drinks;
USE drinks;
CREATE TABLE easy_drinks
(drink_name VARCHAR(16), main VARCHAR(20), amount1 DEC(3,1), second VARCHAR(20), amount2 DEC(4,2), directions VARCHAR(250));
INSERT INTO easy_drinks VALUES
('Blackthorn', 'tonic water', 1.5, 'pineapple juice', 1, 'stir with ice, strain into cocktail glass with lemon twist'), ('Blue Moon', 'soda', 1.5, 'blueberry juice', .75, 'stir with ice, strain into cocktail glass with lemon twist');
NULL
如果在插入statement中忽略掉的值,在table中是以NULL的形式出现。NULL 并不是zero or empty string,同样的NULL is not equall to itself. 可以理解为Unopend box. 也就是说NULL可以看作是一个占位符。说明这个位置的值还没有确定。表示Undefined.
如果在插入数据时,不想让某一个column的值为NULL,那么应该在创建表格时在后面加上NOT NULL,如下:
CREATE TABLE my_contacts
( last_name VARCHAR (30) NOT NULL, first_name VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL
);
DEFAULT
如果我们想在某一个列中不插入特定的值时,使用默认的值进行填充。则可以在创建表格时使用DEFAULT进行说明。default 值应该与设定的类型相一致。例如:
CREATE TABLE doughnut_list (
doughnut_name VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL, doughnut_type VARCHAR(8) NOT NULL, doughnut_cost DEC(3,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1.00
);
DEC(3,2)设定的默认值是1.00。一共有三个数,小数点后面有两位。
知识点
- 在CREATE TABLE 时最后一个category声明的最后不能加
,。是为了说明这是CREATE TABLE 的结束。如果添加了则会报错。 - 不能重复建立相同名称的table
- 最好在TextEditor中写好SQL的语句,然后复制到terminal中。
DROP TABLE my_contacts会把table和其中的数据全部删除。使用此语句一定要慎重。- DATE type 需要特别的格式例如:
'1980-09-05'
SELECT statement
WHERE
SELECT * FROM my_contacts WHERE first_name = 'Anne';
my_contacts: table name WHERE: tells the software you want to look at something specific first_name : you want to look at the value in the column
first_name=: sql isAnne: the value you want to find in columnfirst_name*: star means all columns in the table
在创建表格时,如果data type 设定的是INT or DEC,在使用select 提取时如果是加了括号,那么SQL也会转化成为INT or DEC。这是因为SQL对其有一定的容错率。
These last two queries will work because most SQL RDBMSes give you a little latitude. They will ignore the quotes and treat your DEC and INT values as numbers, even though the quotes indicate they are text values. The queries are NOT CORRECT, but your RDBMS is forgiving.
在使用DATA TYPE 时对于括号问题需要注意如下 The VARCHAR, CHAR, BLOB, DATE, and TIME data types need single quotes. The numeric types, DEC and INT, do not.
括号问题
如果字符中存在单引号,则会引起配对问题。如果想保留字符中的单引号可以在后面加上反斜杠。例如:INSERT INTO my_contacts (location) VALUES ('Grover\'s Mill');. 也可以使用两个单引号,例如INSERT INTO my_contacts VALUES ('Funyon','Steve','steve@onionflavoredrings. com', 'M', '1970-04-01', 'Punk','Grover''s Mill, NJ','Single','smashing the state','compatriots, guitar players');. ‘Grover’’s Mill
在字符串的开始和结束使用单引号,是因为在字符串中存在空格,用单引号可以确定开始和结束。如果字符串中存在单引号,那么SQL就会出现混淆而出错。而数字不需要,因为数字很容易区分开始和结束,中间不存在空格。在MySQL语句中,双引号与单引号的作用相同,可以使用双引号包含单引号。
从网上复制的SQL 命令在粘贴到terminal时应该先粘贴到text editor。然后查看有没有特殊字符,然后删除掉后再复制到terminal中。
AND(combining queries)
使用AND链接两个或者多个queries,例如: SELECT location FROM doughnut_ratings WHERE type='plain glazed' AND rating = 10;
多个AND可以使用括号把中间的条件括起来,以进行区别。如下:
SELECT * FROM my_contacts
WHERE gender = 'F'
AND status = ‘single'
AND state=‘MA'
AND seeking LIKE ‘%single M%'
AND birthday > ‘1950-03-20'
AND birthday < ‘1960-03-20'
AND
(
interest1 = ‘animals'
OR interest2 = ‘animals'
OR interest3 = ‘animals'
OR interest4 = ‘animals'
)
AND
(
interest1 = ‘trading cards'
OR interest2 = ‘trading cards'
OR interest3 = ‘trading cards'
OR interest4 = ‘trading cards'
);
Finding numeric values
在SELECT statement中需要对数字进行处理,这时会用到以下比较运算符:
=: 与column值完全相同才会返回<>: not equal, 不相同时才会返回<: less than>: greater than<=: lessen than or equal to>=:greater than or equal to
Finding text data
text 是按照字母的顺序进行比较,例如想select 以字母‘L’开头的drinks,可以使用如下select statementSELECT drink_name FROM drink_info WHERE drink_name >= 'L' AND drink_name < 'M';
查询并返回drink_name 开头的字母大于等于
L并且小于M。
OR
使用select 在WHERE 条件下,满足任何一个条件都可以使用OR SELECT drink_name from easy_drinks WHERE main = 'cherry juice' OR second = 'cherry juice';
select NULL
直接select NULL values 可以使用IS NULL, 例如SELECT drink_name FROM drink_info WHERE calories IS NULL;
LIKE
LIKE 用于匹配字符串,与wildcard 配套使用。常用的wildcard 有以下两种:
%: The percent is tand in for any number of unknown characters._: The underscore is a stand-in for just one unknown character.
SELECT first_name FROM my_contacts
WHERE first_name LIKE '_im';
SELECT first_name FROM my_contacts
WHERE first_name LIKE '%im';
_im: LIKE Jim, Kim, and, Tim.%im: LIKE Ephraim, Slim, and Tim.
select ranges
如果选择某一范围内的数字的话,有两种方式:
- 使用比较运算符
- 使用
BETWEEN
SELECT drink_name FROM drink_info
WHERE calories >= 30 AND calories <= 60;
SELECT drink_name FROM drink_info
WHERE
calories BETWEEN 30 AND 60;
这两个语句的结果是相同的。需要注意的是
BETWEEN AND的范围是 [30,60],不是(30,60)。即包括两个边界。BETWEEN is equivalent to using the <= and >= symbols, but not the < and > symbols.
对于字母使用BETWEEN,应该注意。例如选择起始字母为G到O的drink_name,则应该使用
SELECT drink_name FROM drink_info WHERE drink_name BETWEEN 'G' AND 'P';
IN / NOT IN
如果有多个候选项,则可以使用IN,把候选项放在括号中。如SELECT date_name FROM black_book WHERE rating IN ('innovative', 'fabulous', 'delightful', 'pretty good');
如果是排除在为,可以使用NOT IN. 例如SELECT date_name FROM black_book WHERE rating NOT IN ('innovative', 'fabulous', 'delightful', 'pretty good');
NOT
NOT 可以和其他条件语句配合使用。但是要放在WHERE,OR,AND之后。例如
SELECT drink_name FROM drink_info WHERE NOT carbs BETWEEN 3 AND 5;
SELECT date_name from black_book WHERE NOT date_name LIKE 'A%' AND NOT date_name LIKE 'B%';
有以上语句可以看出,NOT 放在条件语句的前面,放在OR ,AND 的后面。
NOT IN是一个特殊情况。以下两个语句返回结果相同
SELECT * FROM easy_drinks
WHERE NOT main IN ('soda', 'iced tea');
SELECT * FROM easy_drinks
WHERE main NOT IN ('soda', 'iced tea');
可以使用NOT选择出column中含有NULL的rows。如下:
SELECT * FROM easy_drinks WHERE NOT main IS NULL;
SELECT * FROM easy_drinks WHERE main IS NOT NULL;
DELETE and UPDATE
DELETE
DELETE后面不需要加columns,因为它会把满足条件的所有rows 都删除。因此,DELETE与SELECT一样,可以使用WHERE语句筛选出满足条件的row 然后删除掉。模式为DELETE FROM table_name WHERE expression 例如:
DELETE FROM clown_info WHERE activities = 'dancing';
DELETE 不能删除某一列的数据,只能删除rows。
DELETE FROM your_table; 会删除table中的所有数据。 因此在使用DELETE时,最好先使用SELECT + WHERE相同的选择条件,查看是否是真正想删除的rows。确定以后再使用DELETE进行删除。
UPDATE
UPDATE 是更改满足WHERE条件下的rows的columns的值。如果需要修改多个columns,那么应该使用逗号进行分割。范式为UPDATE table_name SET column1=value1,column2=value2 WHERE expression; , 例如:
UPDATE your_table
SET first_column = 'newvalue',second_column = 'another_value'
WHERE amount1 > 2;
- : 如果忽略掉WHERE,则会改变每个row的column的值,这个column是SET中的column
因为UPDATE也会影响数据,为了保证其正确性,我们可以先使用SELECT查看WHERE语句是否正确。
在SET 中我们可以对numerical 进行基本的数学运算,例如加减乘除。如UPDATE drink_info SET cost = cost + 1 WHERE drink_name='Blue Moon';
同样的,也可以在SET中对string 进行处理,例如UPPER():全部变成大写; LOWER():全部变成小写。例如UPDATE drink_info SET drink_name = UPPER(drink_name) WHERE cost > 5;
Smart Table Design
- A table is all about relationships: how the columns relate to each other to describe a thing.
当创建表格时应该考虑,如何使用column的信息来表述thing。以及你想怎么使用这些数据,使用方法不同,则在设计的时候也会有所不同。广泛采用的策略是:
- Pick your thing, the one thing you want your table to describe.(What’s the main thing you want your table to be about?): 设计的这个table是关于什么的?你想用这个table来表示什么?
- Make a list of the information you need to know about your one thing when you’re using the table.(How will you use this table?):如果表示thing,需要知道哪些信息,然后再把这些信息分割,以及分割的要多细(比如location,是占一个column,还是需要把state独立出来),这需要考虑如何使用这个表格。
- Using the list, break down the information about your thing into pieces you can use for organizing your table.(How can you most easily query this table?): 怎么方便,怎么分割。
- official rules of atomic data
- RULE 1: A column with atomic data can’t have several values of the same type of data in that column.
- RULE 2: A table with atomic data can’t have multiple columns with the same type of data.
以上三个策略和两个rules 是把信息分割成atomic的方法。分割成atomic是normal table 的一部分。
- The benefits of normal tables
- Normal tables won’t have duplicate data, which will reduce the size of your database. : 省空间
- With less data to search through, your queries will be faster. :快
FIRST NORMAL FORM(1NF)
To be 1NF, a table must follow these two rules:
- Each row of data must contain atomic values.
- Each row of data must have a unique identifier, known as a Primary Key.
A primary key is a column in your table that makes each record unique.
The best primary key may be a new primary key. When it comes to creating primary keys, your best bet may be to create a column that contains a unique number.
SHOW TABLES CREATE info
如果我们想查看当前表格是如何建立的我们可以使用如下例句,
SHOW CREATE TABLE table_name;
这会显示create table 的信息,但是不包含里面的内容。
从显示的结果中我们可以得到以下几点信息:
- table name 和 column name 会有backticks 括起来
- 在创建table时如果不写明此column是否是NULL,那么没有赋值时默认是NULL
ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1: 括号结束后的最后一行表明数据是如何保存的,以及使用什么字符。
backtick character的作用是表示column,它可以把SQL的reserved word作为column name。例如
select varchar(50) # won't work
`select` varchar(50) # work , but this is a bad idea
SHOW 的其他用法
SHOW COLUMNS FROM tablename;
SHOW CREATE DATABASE databasename;
SHOW INDEX FROM tablename;
SHOW WARNINGS; # If you get a message on your console that your SQL command has caused warnings, type this to see the actual warnings.
ALTER
添加Primary key
在已有的Table 中添加新的列,如下:
ALTER TABLE your_table
ADD COLUMN id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT FIRST, # 与在CREATE TABLE中定义column 一样,不过没有括号
ADD PRIMARY KEY (id); # 添加
- FIRST : 把此列放在column list 的第一位
- ADD COLUMN : 添加一列
删除PRIMARY KEY
首先应该先去掉AUTO_INCREMENT 这一属性,然后再DROP PRIMARY KEY,然后才可以DROP COLUMN
ALTER TABLE boys
MODIFY toy_id INT;
ALTER TABLE boys
DROP PRIMARY KEY;
ALTER TABLE boys
DROP COLUMN boy_id;
添加新的column
ALTER TABLE my_contacts
ADD COLUMN phone VARCHAR(10) AFTER first_name;
通过AFLTER可以指定新的列添加在哪一列的后面。如果不指定,则默认为添加在最后一列。 You’ve seen that you can use the keywords FIRST and AFTER your_column, but you can also use BEFORE your_column and LAST. And SECOND, and THIRD, and you get the idea.BEFORE and orders after FIRST won’t work with MySQL.也就是说MySQL只能使用
FIRST, AFTER
其他的ALTER 语句
以下命令中COLUMN关键词可以忽略掉。
- RENAME TO
# 更改table 的名称
ALTER TABLE student_info RENAME TO s_info;
- CHANGE COLUMN
既可以改变名称又可以改变此column的类型,例如扩充字符串的长度。
ALTER TABLE project_list
CHANGE COLUMN number proj_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
ADD PRIMARY KEY (proj_id);
使用
CHANGE COLUMN来改变column number to proj_id,然后后面是这一column的类型说明。最后再加上ADD PRIMARY KEY (proj_id)。使其确定primary key。
如果有多个column name 需要修改,则可以在一个query 语句中进行。如下:
ALTER TABLE project_list
CHANGE COLUMN descriptionofproj proj_desc VARCHAR(100),
CHANGE COLUMN contractoronjob con_name VARCHAR(30);
Note:如果修改后的data type 与原有的data type不兼容,则会报错。如果兼容则可能会发生数据丢失。例如:But worse news is that if they are compatible types, your data might be truncated. For example: going from varchar(10) to char(1), your data will change from ‘Bonzo’ to just ‘B’ The same thing applies to numeric types. You can change from one type to another, but your data will be converted to the new type, and you may lose part of your data!
因此在修改数据类型时因定要注意。
- MODIFY COLUMN
MODIFY COLUMN 可以用于改变column 的类型 和column 的顺序。
# 改变类型
ALTER TABLE project_list
MODIFY COLUMN proj_desc VARCHAR(120);
# 改变顺序
ALTER TABLE project_list
MODIFY COLUMN color AFTER model;
change the order using modify is complex : Your software is actually doing a bunch of commands behind the scenes. It is copying the values from the column you wish to move, saving them into a temporary table, dropping the column you wish to move, altering your table and creating a new column with the same name as the old one where you want it to be, copying all the values from the temporary table back into your new column, and deleting the temporary table.
- DROP COLUMN
ALTER TABLE project_list
DROP COLUMN start_date;
除了DROP COLUMN,也可以用于primary key
ALTER TABLE your_table
DROP PRIMARY KEY;
- 修改 AUTO_INCREMENT
# 增加
ALTER TABLE your_table
CHANGE your_id your_id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT;
# 删除,仅仅是重写一遍
ALTER TABLE your_table
CHANGE your_id your_id INT(11) NOT NULL;
Note:It’s important to keep in mind that you can only have one AUTO_INCREMENT field per table, it has to be an INTEGER data type and it can’t contain NULL.
- 删除PRIMARY KEY
首先修改column不再AUTO_INCREMENT,然后再DROP PRIMARY KEY。如下:
ALTER TABLE boys
MODIFY boy_id INT NOT NULL; # 不填写AUTO_INCREMENT
ALTER TABLE boys
DROP PRIMARY KEY;
STRING functions
IMPORTANT: string functions do NOT change the data stored in your table; they simply return the altered strings as a result of your query.
string function 不改变table 的内容。只是返回改变后的结果。
RIGHT(string,num)
从string右边截取num个字符。 例如:
SELECT RIGHT('abcdef', 2); # 返回ef
SELECT RIGHT(location, 2) FROM my_contacts;
location: 为my_contacts 中的column name。此句为截取 location column中的字符串右侧两个字符。
同理,RIGHT可以更换为LEFT。
SUBSTRING_INDEX(string,split,num)
截取string 在分割符split之前的所有字符。num表示在第几个split进行分割。例如
SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX(location, ',', 1) FROM my_contacts;
location: column name in my_contacts ‘,’: comma act as the split here 1 : means split the string in the first comma ex: location is ‘Large City, NY’, the return value is ‘Large City’.
SUBSTRING(your_string, start_position, length)
gives you part of your_string, starting at the letter in the start_position. length is how much of the string you get back.
SELECT SUBSTRING('San Antonio, TX', 5, 3); # return 'Ant'
UPPER(your_string) and LOWER(your_string)
will change everything in the string to uppercase or lowercase, respectively.
SELECT UPPER('uSa'); # return : 'USA'
SELECT LOWER('spaGHEtti'); # return 'spaghetti'
REVERSE(your_string)
it reverses the order of letters in your string.
SELECT REVERSE('spaGHEtti'); # return:ittEHGaps
LTRIM(your_string) and RTRIM(your_string)
returns your string with extra spaces removed from before (to the left of) or after (to the right of) a string.删除左侧/右侧空格
SELECT LTRIM(' dogfood '); # return 'dogfood '
SELECT RTRIM(' catfood '); # return : ' catfood'
LENGTH(your_string)
returns a count of how many characters are in your string.
SELECT LENGTH('San Antonio, TX '); # return 16
Advanced SELECT
使用一些function可以让数据处理变得简单。
CASE
使用CASE的目的是查看满足多个条件时的情况。如果使用UPDATE则当判断多个条件时要写很多个UPDATE,且UPDATE的顺序与你的结果是有关系的。当然CASE是以遇到的第一个为准,而UPDATE是以遇到的最后一个为准。
UPDATE my_table
SET new_column =
CASE # 判断条件的开始
WHEN column1 = somevalue1 THEN newvalue1
WHEN column2 = somevalue2 THEN newvalue2
ELSE newvalue3
END; # 判断的结束
Note: WHEN 之间没有逗号进行分割 如果没有ELSE,则在都不满足的情况下会填充NULL.因为没有什么改变 You can use a CASE expression with
SELECT, INSERT, DELETE,and, as you’ve seen, UPDATE.
如果在END之后添加WHERE则是在满足WHERE条件之下的ROW进行CASE 判断。
ORDER BY
对coloumn的内容进行排序
SELECT title, category FROM movie_table
WHERE category = 'family'
ORDER BY title;
对筛选出来的内容进行排序。ORDER BY 可以对多个columns 进行排序。如下:
SELECT title, category, purchased FROM movie_table
ORDER BY category, purchased;
SELECT title, purchased FROM movie_table
ORDER BY purchased DESC, title ASC;
首先对category 进行排序,然后在对purchased date 进行排序。 默认是从小到大进行排序:By default, SQL returns your ORDER BY columns in ASCENDING order. date : by date, with the oldest date first. Dates are always sorted by year, then by month, then by day. 如果想对column的内容进行降序排列,则只需在column name 后面添加
DESCDESC (DESCENDING) ; ASC(ascending) DESC 放在table 前面是DESCRIBE; 放在column 后面是降序排列,不过在SQL中降序排列不能使用DESCENDING,只能使用DESC。
SUM(column_name)
针对某一列中的值进行求和,例如:
SELECT SUM(sales) FROM cookie_sales
WHERE first_name = 'Nicole';
GROUP BY(column_name)
把相同的first_name整合在一起。
SELECT first_name, SUM(sales) FROM cookie_sales
GROUP BY first_name
ORDER BY SUM(sales) DESC;
ORDER BY SUM(sales) DESC: 可以认为SUM(sales)是一列,然后对其进行降序排列。在显示的结果中,在名称一栏也是写着
SUM(sales)
AVG with GROUP BY
SELECT first_name, AVG(sales) FROM cookie_sales
GROUP BY first_name;
MIN and MAX
MAX: 在column中找出最大值 MIN:在column中找出最小值
SELECT first_name, MAX(sales) FROM cookie_sales
GROUP BY first_name;
SELECT first_name, MIN(sales) FROM cookie_sales
GROUP BY first_name;
COUNT
COUNT计算在一个column下有多少rows。如果在column中的value是NULL,则不计算在内。
SELECT COUNT(sale_date) FROM cookie_sales;
SELECT first_name, COUNT(sale_date) FROM cookie_sales
GROUP BY first_name;
WHERE sales > 0;
WHERE 条件放到最后
DISTINCT
DISTINCT 是一个关键词,而不是一个function,因此不需要使用括号把column name 括起来。 DISTINCT is a keyword and not a function, you don’t need parentheses around sale_date.
SELECT DISTINCT sale_date FROM cookie_sales
ORDER BY sale_date;
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT name) FROM sales
DISTINCT name 要放在COUNT括号内。
如果column 中存在NULL,则DISTINCT keyword 会把NULL显示出来。但是像COUNT,MAX,MIN,AVG,SUM等function并不会把NULL计算在内。
LIMIT num
LIMIT 限定了返回多少行。LIMIT allows us to specify exactly how many rows we want returned from our result set.
SELECT first_name, SUM(sales) FROM cookie_sales
GROUP BY first_name
ORDER BY SUM(sales)DESC
LIMIT 2; # 只输出两行
LIMIT n1,n2: n1 表示返回结果的起始位置,n2表示返回多少。LIMIT start from zero. 如果只是一个数,那么可以认为忽略了0,例如LIMIT 2可以看作是LIMIT 0,2. 例如,有1000首歌曲对流行度进行排序,查看20到30的流行歌曲是什么。可以用LIMIT 19,10.
multi-table database design
对于不是atomic的colum我们把它独立出来,并形成新的table。 We need to move the non-atomic columns in our table into new tables.
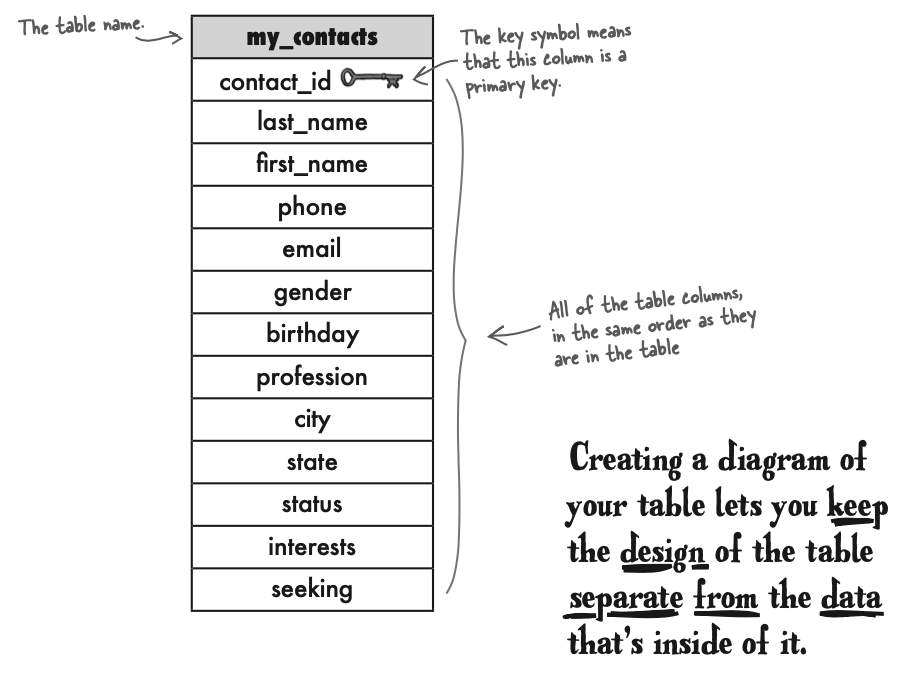
schema
schema 是在一个database中使用table和columns,以及table之间的关系。 A representation of all the structures, such as tables and columns, in your database, along with how they connect, is known as a schema.
A description of the data (the columns and tables) in your database, along with any other related objects and the way they all connect is known as a SCHEMA
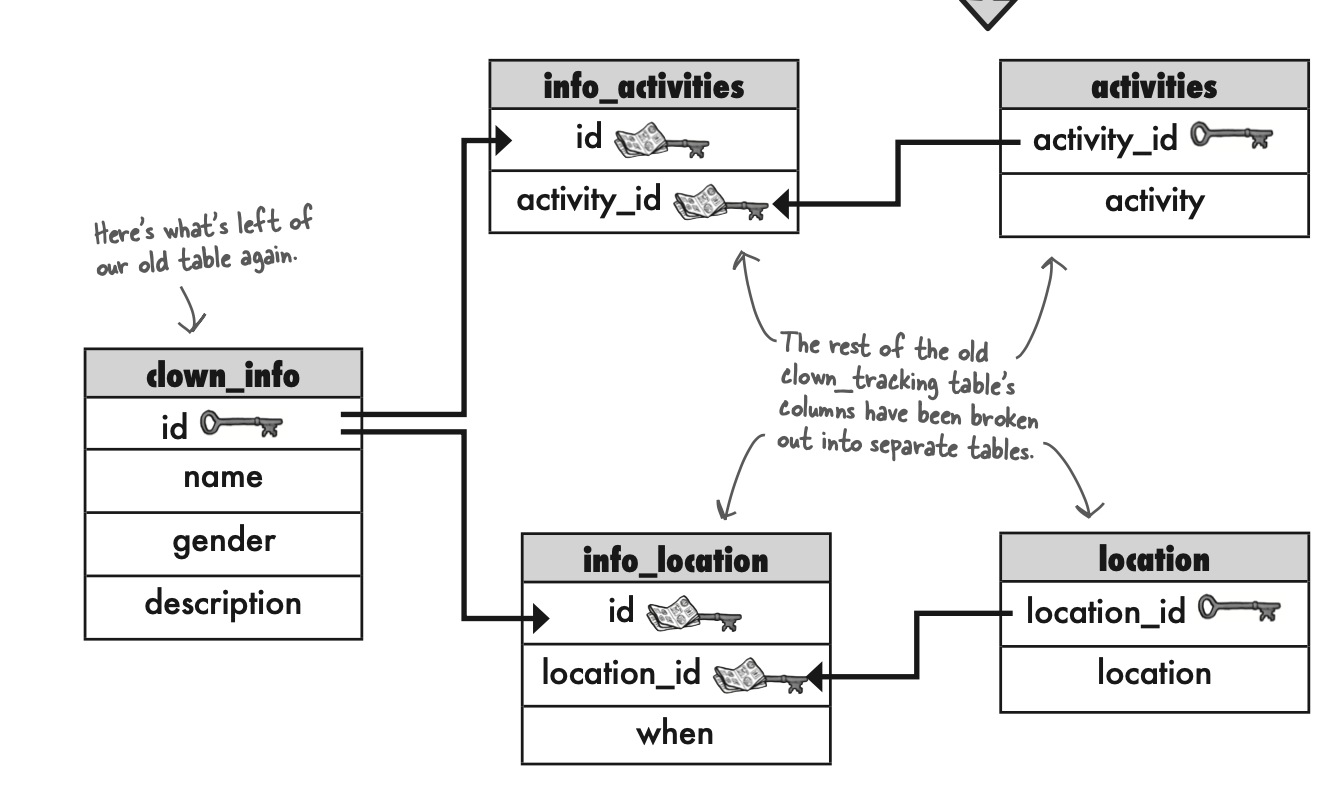
为了直观的表示一个table,可以使用schema,如下:
Foreign Key
Foreign key 告诉我们在这一行的数据在另一个表格中属于哪一行。 The FOREIGN KEY is a column in a table that references the PRIMARY KEY of another table.
Foreign key fatct:
A foreign key can have a different name than the primary key it comes from. The primary key used by a foreign key is also known as a parent key. The table where the primary key is from is known as a parent table. The foreign key can be used to make sure that the rows in one table have corresponding rows in another table. Foreign key values can be null, even though primary key values can’t. Foreign keys don’t have to be unique—in fact, they often aren’t.
A NULL foreign key means that there’s no matching primary key in the parent table.
You can use a foreign key to reference a unique value in the parent table. It doesn’t have to be the primary key of the parent table, but it must be unique.
创建有Foreign key 表格,如下:
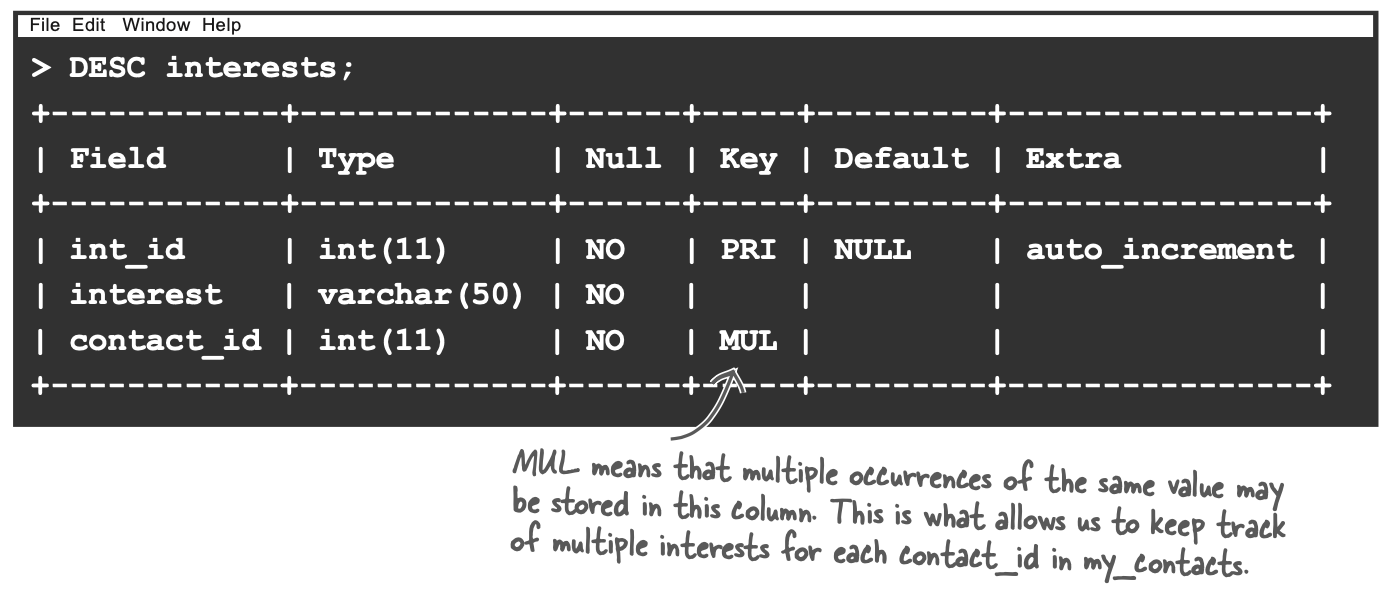
CREATE TABLE interests
(
int_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
interest VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
contact_id INT NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT my_contacts_contact_id_fk
FOREIGN KEY (contact_id)
REFERENCES my_contacts (contact_id)
);
CONSTRAINT: 用以说明foreign key 是来自哪个表格。如果想法改变了,这个名称可以帮助我们undo it。
FOREIGN KEY : 关键词,用以说明外键是哪一个。
REFERENCES: 定义外键来自于哪个表格。
如果想删除parent table中的数据,则需要确认其primary key 在children table 中的foreign key 不存在。如果存在则会出现error。
之所以创建FOREIGN KEY constraint,是因为FOREIGN KEY只能来源于PARETN table,如果在parent table 中primary key 发生变化,则会产生error。
因此如果想在parent table中删除某一primary key,则先在children table中把相关的foreign key 的rows 删除掉。然后再删除parent table 中的rows。如果不在children table里面删除,则会使其query 变慢。
在已有的table 中添加FOREIGN KEY
ALTER TABLE boys
ADD FOREIGN KEY(toy_id) REFERENCES toys(toy_id);
如果是新创建的一个column,然后再使其成为FOREIGN KEY需要分两步进行:
- 使用一个query创建一个column
- 再次水用一个query ADD FOREIGN KEY
ALTER TABLE toys
ADD COLUMN boy_id INT;
ALTER TABLE toys
ADD CONSTRAINT boys_boy_id FOREIGN KEY(boy_id) REFERENCES boys(boy_id);
删除FOREIGN KEY
首先DROP 掉一个column,如果这个column 是FOREIGN KEY,则应该先通过CONSTRAINT 删除掉这一FOREGIN KEY 的属性,然后再删除掉这一column。
ALTER TABLE toys
DROP FOREIGN KEY boys_boy_id;
ALTER TABLE toys
DROP COLUMN boy_id;
boys_boy_id 是FOREGIN KEY 的CONSTRAINT 的名称,在这里可以看出CONSTRAINT 的作用来了。 boy_id 是当作FOREIGN KEY的column name,此时可以按照正常的drop column 来进行删除。参考stack overflow
应该使用
ADD来添加FOREGIN KEY, 与添加PRIMARY KEY 是一致的。同时也应该使用REFERENCES 来表明FOREIGN KEY 来自于哪一个table。可以参考stack overflow
Relationships between tables
数据之间的关系(即table与table之间的关系)有以下三种:一对一(one to one),一对多(one to many), 多对多(many to many)。
Patterns of data: one-to-one
即在table A中的记录,在Table B 中有且仅有一个记录。例如员工表,和工资表。 One-to-One: exactly one row of a parent table is related to one row of a child table.
为什么会有一对一的关系:
- 把关心的数据单独放在一张表格中,那么查询起来更快。Pulling the data out may allow you to write faster queries. For example, if most of the time you need to query the SSN and not much else, you could query just the smaller table.
- 在建立表格时,有些column的数据不确定,可以分离出去,避免在table中出现NULL值。 If you have a column containing values you don’t yet know, you can isolate it and avoid NULL values in your main table.
- 为了安全考虑,把敏感数据放到一张表格中。 You may wish to make some of your data less accessible. Isolating it can allow you to restrict access to it. For example, if you have a table of employees, you might want to keep their salary information out of the main table.
- 长文本数据单独放在一个表格中。 If you have a large piece of data, a BLOB type for example, you may want that large data in a separate table.
Patterns of data: one-to-many
One-to-Many: a record in Table A can have MANY matching records in Table B, but a record in Table B can only match ONE record in Table A.
Patterns of data: getting to many-to-many
像女生的鞋子品牌表格和女生拥有的鞋子的品牌表格之间的关系。
为了把many to many table 转化成一对多的关系,我们需要建立一个junction table。来连接两个表格。And then turn the many-to-many relationship into two one-to-many relationships.
the secret of the many-to-many relationship—it’s usually made up of two one-to-many relationships, with a junction table in between.
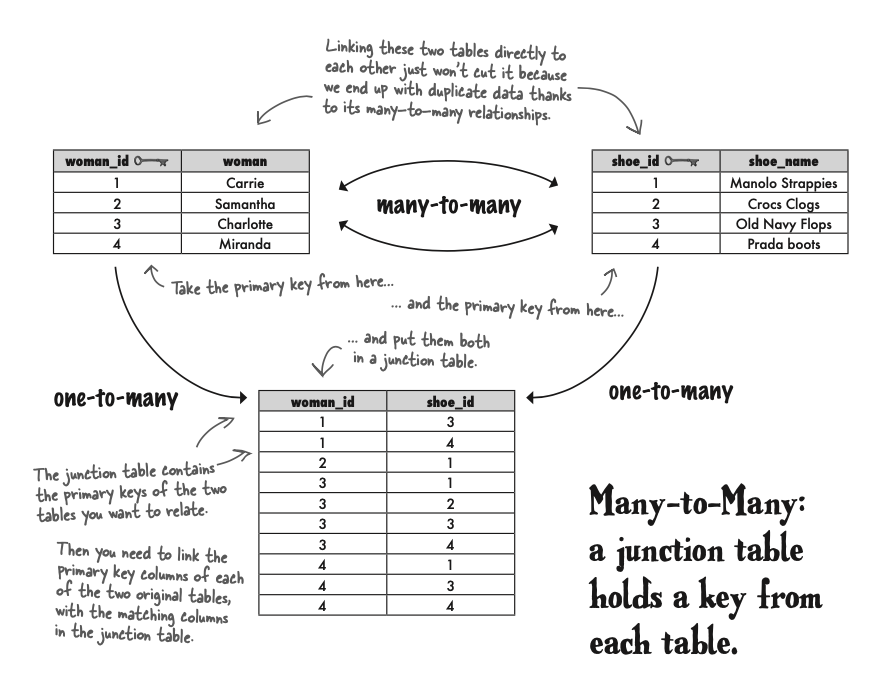
Junction table 的好处
- 保持数据的完整性。例如my_contacts, contact_interest, interest 这三个表格。contact_interest是junction table。如果我想要在my_contacts中删除一个联系人,那么只需要删除my_contacts 和contact_interest中的数据即可。不需要涉及interest table。这样减少误差。
- 修改数据方便。例如在interest中一个爱好的拼写写错了,只需要在interest table中修改即可。与其他两个表格没有关系。
composite key
A key made of two or more columns is known as a composite key.A COMPOSITE KEY is a PRIMARY KEY composed of multiple columns, creating a unique key.
Functionally dependent
When a column’s data must change when another column’s data is modified, the first column is functionally dependent on the second.
A quick way to describe a functional dependency is to write this: T.x —> T.y(in the relational table called T, column y is functionally dependent on column x.)
A partial functional dependency means that a non-key column is dependent on some, but not all, of the columns in a composite primary key.
Transitive functional dependency: when any non-key column is related to any of the other non-key columns.
second normal form
second normal form focuses on how the primary key in a table relates to the data in it.
Your 1NF table is also 2NF if all the columns in the table are part of the primary key OR It has a single column primary key
Second Normal Form or 2NF:
Rule 1: Be in 1NF Rule 2: Have no partial functional dependencies.
If your table has an artificial primary key and no composite primary key, it’s in 2NF(认为合成的primary key,并且不存砸composite primary key 就可以认为是满足2NF)
Third Normal Form or 3NF:
Rule 1: Be in 2NF Rule 2: Have no transitive dependencies
ORDER BY always needs to be last.
在下面的例子中,我们把my_contacts这个表格进行分解,分解为3NF。
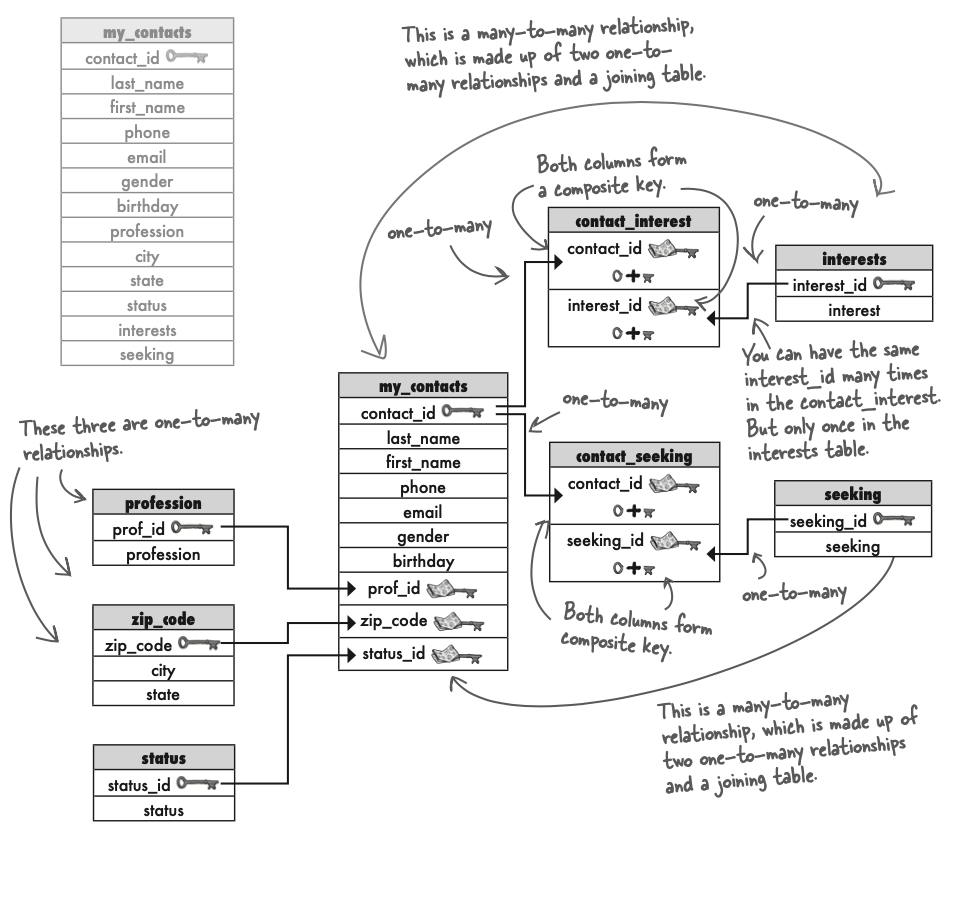
- profession 与 contact_id 存在1对多的关系:一个profession可以对应多个contact_id。因此需要把profession独立出来形成一个新的表格。同样的,state,city,status也存在这样的关系,因此把他们也都独立出来形成新的表格。在state,city中使用zip code作为primary key。
- interest这一column的内容违反了1NF。并且与contact_id存在多对多的关系。即1gecontact_id可以有多个interests;同样的同一个interest也可有很多人具有。因此这是一个多对多的关系。需要使用三个表,使其变成两个一对多的关系。junction table是使用两个table中的primary key 组成的多对多的composite key。
- 实心的箭头指向的表格表示1对多的关系。例如profession与my_contacts是一对多的关系,指向my_contacts的表格的是箭头。
8. joins and multi-table operations
三种创建表格和插入数据的方式
- CREATE TABLE, then INSERT with SELECT
先创建table,然后插入数据
CREATE TABLE profession (
id INT(11) NOT NULL
AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
profession varchar(20)
);
INSERT INTO profession (profession)
SELECT profession FROM my_contacts
GROUP BY profession
ORDER BY profession;
- CREATE TABLE with SELECT, then ALTER to add primary key
创建表格的同时插入数据,然后再修改表格。
CREATE TABLE profession AS
SELECT profession FROM my_contacts
GROUP BY profession
ORDER BY profession;
ALTER TABLE profession
ADD COLUMN id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT FIRST,
ADD PRIMARY KEY (id);
- CREATE TABLE with primary key and with SELECT all in one
创建表格和插入数据同时进行
CREATE TABLE profession (
id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
profession varchar(20)
) AS
SELECT profession FROM my_contacts
GROUP BY profession
ORDER BY profession;
这里需要注意的是create table 中的profession column的名称需要与select 中的column的名称相同。如果不同则会自动插入select 中的column的名称。为了修改名称,可以使用AS,如下:
CREATE TABLE profession
(
id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
zhiye VARCHAR(20)
) AS
SELECT profession AS zhiye FROM my_contacts
GROUP BY zhiye
ORDER BY zhiye;
AS populates a new table with the result of the SELECT. So when we used AS in the second and third examples, we were telling the software to take all the values that came out of the my_contacts table as a result of that SELECT and put it into a new profession table we just created. If we hadn’t specified that the new table have two columns with new names, AS would have created just one column, filled with the same name and data type as the column that’s the result of the SELECT.
aliases
临时给column 或者table起一个新的名字。方法就是在原来的名称后面添加AS,然后在后面再添加你想添加的名称。
由于是临时的名称,因此SELECT并不会改变原始table中的名称。
Table alias的意义在于使用多个table时指定某个table更方便。方法如给column alias相同。就是在原有table name后面添加AS,然后再在后面添加你想临时使用的table name。
其实给column 和 table起临时的名称可以省略掉AS。如下:
SELECT profession mc_prof
FROM my_contacts mc
GROUP BY mc_prof
ORDER BY mc_prof;
Cartesian join
it has other names like : Cartesian product, cross product, cross join.
The CROSS JOIN returns every row from one table crossed with every row from the second.
SELECT t.toy, b.boy
FROM toys AS t
CROSS JOIN
boys AS b;
CROSS JOIN can just leave out, 结果时相同的。 like below:
SELECT toys.toy, boys.boy
FROM toys,boys;
toys.toy: comma之前是table的名称,之后是column的名称。与dataframe中的引用方式一致。
生成的结果中column name 则为toy, boy。是与table后面的column name一致。
INNER JOIN
An INNER JOIN is a CROSS JOIN with some result rows removed by a condition in the query.
SELECT somecolumns
FROM table1
INNER JOIN
table2
ON somecondition;
NOTE: 在table后面可以添加alias,ON可以更换为WHERE,结果是一样的。
An INNER JOIN combines the records from two tables using comparison operators in a condition.
-
EQUIJOINinner joins test for equality. 可以看作是使用等式的INNER JOIN。 -
non-equijoin: inner joins test for inequality. 例如toys和boys。我们可以使用non-equijoin来查看每个boy 没有的toys。然后在他过生日的时候给他买没有的toy。
SELECT boys.boy, toys.toy
FROM boys
INNER JOIN
toys
ON boys.toy_id <> toys.toy_id
ORDER BY boys.boy;
natural join: Natural joins only work if the column you’re joining by has the same name in both tables. NATURAL JOIN inner joins identify matching column names.
SELECT boys.boy, toys.toy
FROM boys
NATURAL JOIN
toys;
subqueries
A subquery is a query that is wrapped within another query. It’s also called an INNER query.A subquery is nothing more than a query inside another query.
SELECT last_name, first_name FROM my_contacts
WHERE zip_code =
(
SELECT zip_code FROM zip_code
WHERE city = 'Memphis' AND state = 'TN'
)
在上面的例子中,WHERE 条件句中我们使用的是=,因此subquery 中返回的应该是一个scalar值(即 one column one row)。如果是IN,例如WHERE zip_code in (SELECT zip_code FROM zip_code WHERE state = 'TN')。因此subquery 到底应该返回什么是根据条件句式进行调整的。
以上例句同样可以使用INNER JOIN,但是有的人认为以上句式更好理解。
SELECT last_name, first_name
FROM my_contacts mc
NATURAL JOIN
zip_code zc
WHERE zc.city = 'Memphis' AND zc.state = 'TN'
在subquery 中如果SELECT column name比较长,我们可以使用AS 取一个容易记住的名字。
A subquery as a SELECT column
SELECT mc.first_name, mc.last_name,
(SELECT state
FROM zip_code WHERE mc.zip_code = zip_code) AS state
FROM my_contacts mc;
以上例句中(SELECT state FROM zip_code WHERE mc.zip_code = zip_code) AS state) 充当了新的一列,并且起了一个新名称state
我们到现在看到的subqueries都是noncorrelated。这种情况下,inner query 会先执行,因为它与outer query 没有关系。但是outer query 的执行要依赖于inner query。 noncorrelated subqueries: The inner query gets processed first, then the result is used in the WHERE condition of the outer query. But the inner query in no way depends on values from the outer query; it can be run as a standalone query.
joins are more efficient than subqueries.
A noncorrelated subquery with multiple values: IN, NOT IN
A noncorrelated subquery uses IN or NOT IN to test if the values returned in the subquery are members of a set (or not).
SELECT mc.first_name, mc.last_name, mc.phone, jc.title
FROM job_current AS jc
NATURAL JOIN
my_contacts AS mc
WHERE jc.title IN (SELECT title FROM job_listings);
IN evaluates each row of jc.title values against the entire set returned by the subquery.
SELECT mc.first_name, mc.last_name, mc.phone, jc.title
FROM job_current jc
NATURAL JOIN
my_contacts mc
WHERE jc.title NOT IN (SELECT title FROM job_listings);
NOT IN returns any current job titles that are not found in the job listings.
做题
based on the table’s relation, answer the following questions.
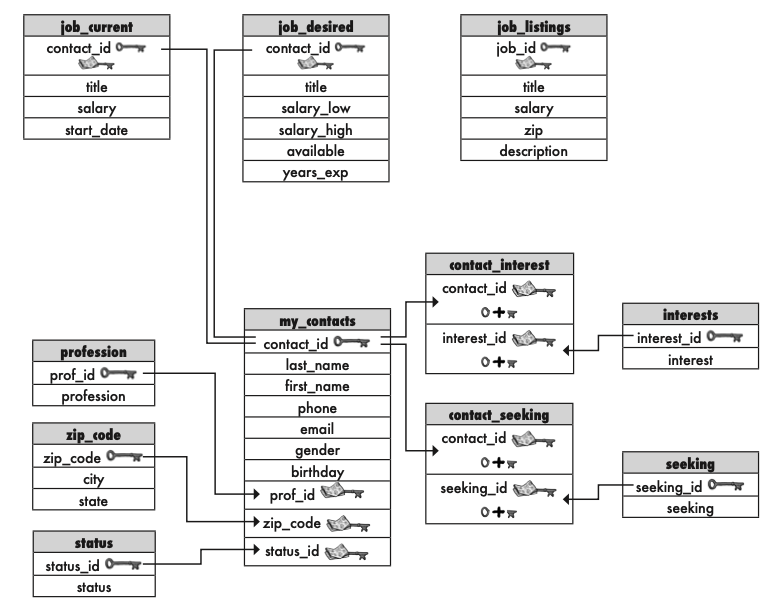



Correlated subqueries
A correlated subquery means that the inner query relies on the outer query before it can be resolved.
Correlated subqueries 的完成需要依赖于outer query。
SELECT mc.first_name, mc.last_name
FROM my_contacts AS mc
WHERE
3 = ( SELECT COUNT(*) FROM contact_interest WHERE contact_id = mc.contact_id
);
The subquery depends on the outer query. It needs the value for contact_id from the outer query before the inner query can be processed. It uses the same alias or correlation name for my_contacts, mc, that was created in the outer query.
如果subqueries 使用outer query 中的table中的alias,那么彼此将相互依赖形成Correlated subqueries 。
EXISTS and NOT EXISTS
这两个的用法与IN / NOT IN相同,放在条件语句的前面,后面一般是跟括号括起来的subquery。
A very common use for correlated subqueries is to find all the rows in the outer query for which no rows exist in a related table.
Just like with IN and NOT IN, you can both use EXISTS and NOT EXISTS with your subqueries.
SELECT mc.first_name firstname, mc.last_name lastname, mc.email email
FROM my_contacts mc
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM contact_interest ci WHERE mc.contact_id = ci.contact_id );
The query below returns data from my_contacts where the contact_ids show up at least once in the contact_interest table.
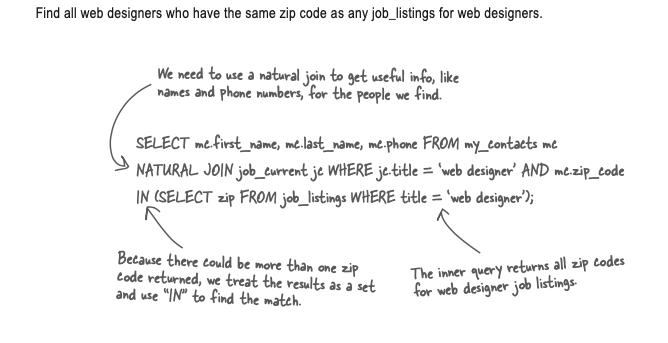
构建Subquery 的方法是先把问题拆解成简单的。然后再把subquery 带入。 例如:If you’re trying to find people who earn the same amount of money as the highest paid web designer, break it apart into:
- Find the highest paid web designer
- Find people who earn x amount of money
outer joins, self-joins, and unions
outer joins 是处理两个tables 之间的关系。
LEFT OUTER JOIN
A LEFT OUTER JOIN takes all the rows in the left table and matches them to rows in the RIGHT table.
In a LEFT OUTER JOIN, the table that comes after FROM and BEFORE the join is the LEFT table, and the table that comes AFTER the join is the RIGHT table.

The left outer join matches EVERY ROW in the LEFT table with a row from the right table.
INNER JOIN 与 OUTER JOIN的区别
The difference is that an outer join gives you a row whether there’s a match with the other table or not.
A NULL value in the results of a left outer join means that the right table has no values that correspond to the left table.
反正left table中的SELECT column 会全部输出,如果与right table 没有对应的,则在相应的row中会输出NULL。
LEFT OUTER JOIN 中使用的条件语句在MySQL中应该使用ON,好像WHERE是不行的。
RIGHT OUTER JOIN
The right outer join is exactly the same thing as the left outer join, except it compares the right table to the left one. The two queries below give you precisely the same results:
SELECT g.girl, t.toy
FROM toys t
RIGHT OUTER JOIN
girls g
ON g.toy_id = t.toy_id;
SELECT g.girl, t.toy
FROM girls g
LEFT OUTER JOIN
toys t
ON g.toy_id = t.toy_id;
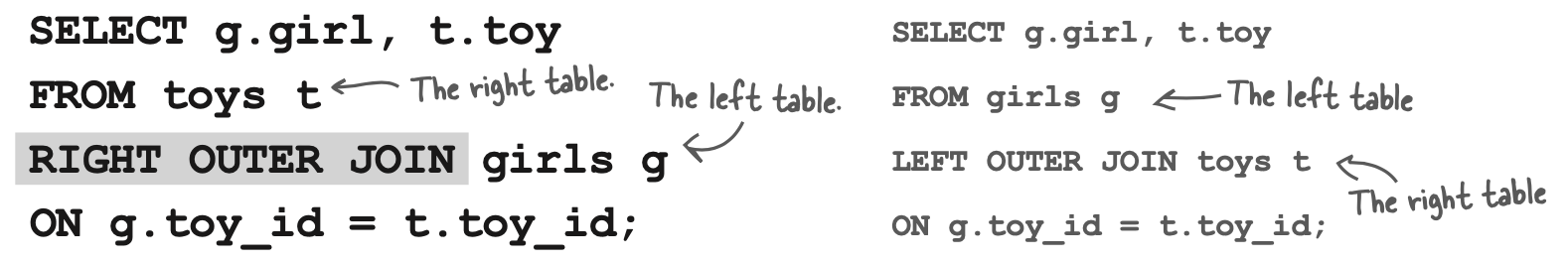
对于个人来说,最好是坚持使用一个OUTER JOIN,这样可以避免混淆。但是也应该理解两个OUTER JOIN 的区别。
self-referencing foreign key
The self-referencing part means that it is a key that is referencing another field in the same table.
A self-referencing foreign key is the primary key of a table used in that same table for another purpose.
self-referenceing foreign key就是把当前table中某一列作为这个表格的foreign key。
self-join
self-join 就是使用一个表格但是给它起了两个不同的别名。这样就可以当作两个相同的表格使用。
The self-join allows you to query a single table as though there were two tables with exactly the same information in them.
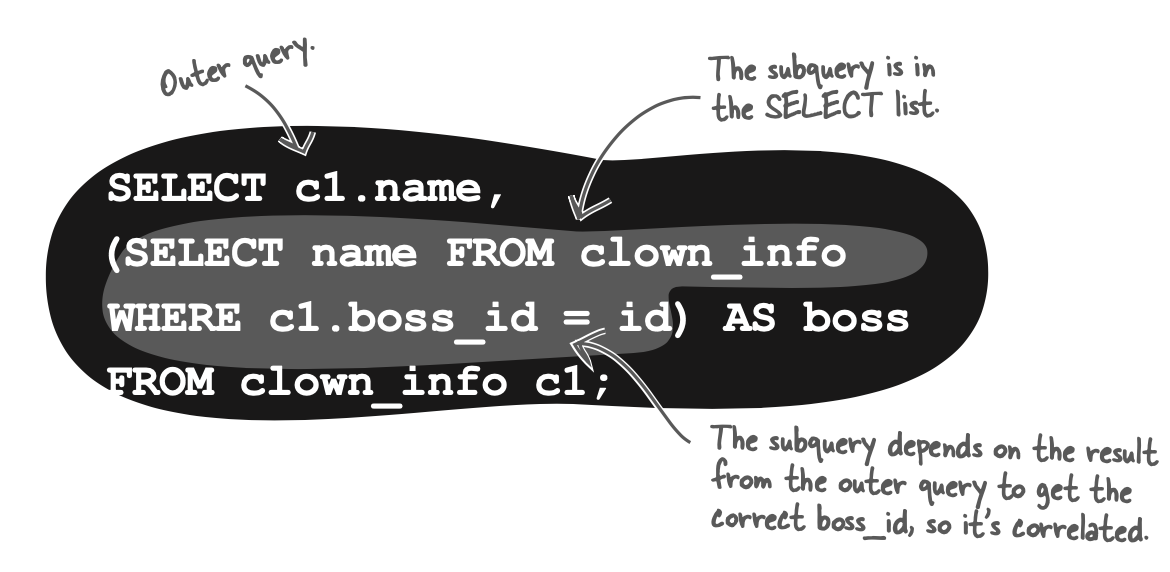
SELECT c1.name, c2.name AS boss
FROM clown_info c1
INNER JOIN
clown_info c2
ON c1.boss_id = c2.id;
self-join可以转化成subquery,如下:
UNION
UNION 可以把两个或者多个表格变成一个表格。并且会删除重复的数据。
SELECT title FROM job_current
UNION
SELECT title FROM job_desired
UNION
SELECT title FROM job_listings;
UNION can only take one ORDER BY at the end of the statement. This is because UNION concatenates and groups the results from the multiple SELECT statements.
SELECT title FROM job_current
UNION
SELECT title FROM job_desired
UNION
SELECT title FROM job_listings
ORDER BY title;
由于是concatenates,因此从每个表格中SELECT 出来的column数量应该是一样的,且类型是以应的或者是可以互相转化的。因为UNION 会删除重复数据,因此SELECT 的顺序并不重要。
如果select 中的column 的数据类型是不一致的,至少是可以转化成为统一的。例如INT 和VARCHAR,VARCHAR 不能转化成 INT,但是INT 可以转化成VARCHAR。
If for some reason you DO want to see duplicates, you can use the operator UNION ALL. It returns every match, not just the distinct ones.
SELECT title FROM job_current
UNION ALL
SELECT title FROM job_desired
UNION ALL
SELECT title FROM job_listings
ORDER BY title;
CREATE TABLE AS
如果UNION的column 数据类型不一致,我们想查看转化后的数据类型,需要先建立table。
The CREATE TABLE AS statement takes the results of a SELECT query and makes a table out of them.In the example below, we are putting our title UNION into a new table named my_union.
CREATE TABLE my_union AS
SELECT title FROM job_current
UNION
SELECT title FROM job_desired
UNION SELECT title FROM job_listings;
my_union: table name
INTERSECT and EXCEPT
These two operations DO NOT EXIST in MySQL.
INTERSECT and EXCEPT are used in much the same way as UNION—to find parts of queries that overlap.
INTERSECT: returns only those columns that are in the first query and also in the second query.EXCEPT: returns only those columns that are in the first query, but not in the second query.
Defensive Databases part 1
在插入信息时的注意事项,以下可参考
- 如果primary key 是Auto_increment,则可以使用
''代替其位置,表示可以自动填充。好像MySQL没有此功能 - 如果不知道的信息,可以使用特殊字符替代,例如上面例子中,不知道性别,可以使用
X替代。
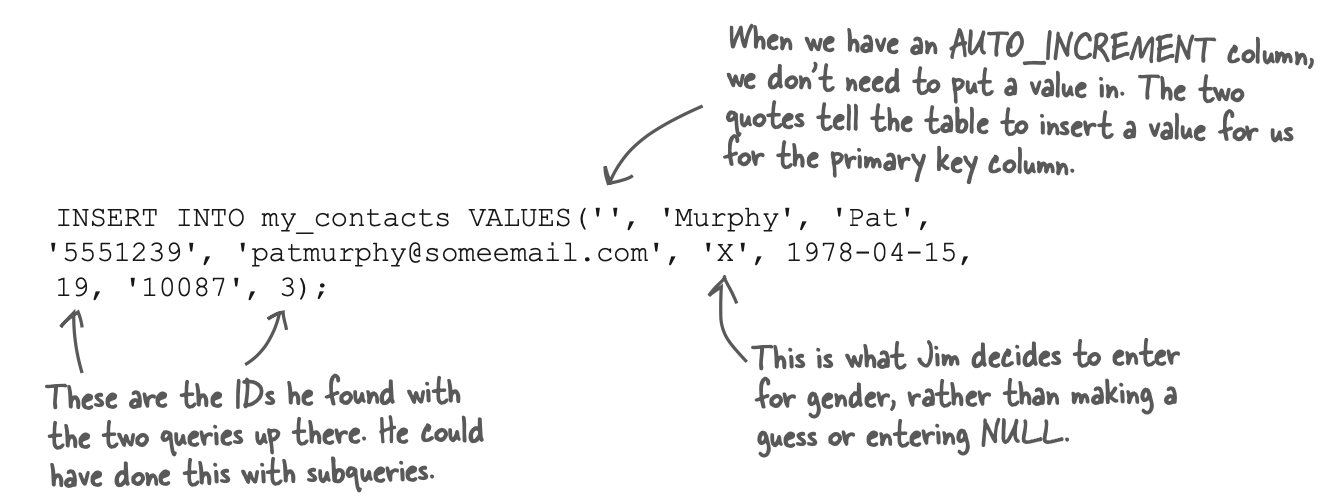
使用subquery 在一个query 中完成
INSERT INTO my_contact
(last_name,first_name,phone,email,birthday,prof_id,zip_code,status_id)
VALUES(
'Pat','Murphy','555-1239','pathmurphy@someemail.com','1978-4-15',
(SELECT prof_id FROM profession WHERE LOWER(profession) = 'teacher'), # prof_id
10087,
(SELECT status_id FROM status WHERE LOWER(status) = 'married') # status_id
);
CHECK CONSTRAINT
A constraint is a restriction on what you can insert into a column. Constraints are added when we create a table.
CONSTRAIN 就是在把column 中的值设定在某一个set 中
已经学过的CONSTRAINT:
- NOT NULL
- PRIMARY KEY
- FOREIGN KEY
- UNIQUE
这次要学习的是CHECK。A CHECK constraint restricts what values you can insert into a column. It uses the same conditionals as a WHERE clause.
CREATE TABLE piggy_bank
(
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
coin CHAR(1) CHECK (coin IN ('P','N','D','Q'))
)
Check 后面添加的是条件,并把它放在括号中。因为CHECK 与WHERE 的情况类似,因此You can use all the conditionals: AND, OR, IN, NOT, BETWEEN and others. 添加上CHECK,就会检查coin值是否在这四个选项中。如果不存在就会报错,然后不会插入任何东西。 在MySQL 8.0.16之前的版本中CHECK功能是不存在的,即使写上CHECK,MySQL也会自动忽略掉。之后的版本已经有了CHECK功能。
view
view的目的是保存经常使用过的query。这样可以方便使用。
Creating a view is really simple. We add a CREATE VIEW statement to our query.
CREATE VIEW web_designers AS
SELECT mc.first_name, mc.last_name, mc.phone, mc.email
FROM my_contacts mc
NATURAL JOIN
job_desired jd
WHERE jd.title = 'Web Designer';
To see what’s in it, we simply treat it as though it were a table. We can use a SELECT:
SELECT * FROM web_designers;
view 的创建与使用AS创建新的table是一样的。同样的也可以把view看作是一个table,不过这个table是根据其他的表格动态变化的。查看时只需要使用SELECT选择所有的行即可。然而SELECT中FROM的table name,我们可以看作是一个subquery。
SELECT * FROM
(SELECT mc.first_name, mc.last_name, mc.phone, mc.email
FROM my_contacts mc
NATURAL JOIN
job_desired jd
WHERE jd.title = 'Web Designer')
AS web_designers;
由于select后面需要跟一个table,但是我们的subquery返回的是一个virtural talbe。如果没有后面的AS web_designers,则SELECT不会起作用,抓取不到东西。因为view 是一个虚拟的table,因此任何在table中的操作也可以使用在view中。虚拟table并不存在与database中,当使用view时只是临时创建了一个table,不使用时则会删除,相当于我们linux系统中的temp文件中的东西。这样的好处是,当有新的信息加入时,通过view也可以看到。
And while our SELECT statement results in a virtual table, there’s no way that SQL can grab onto it without that alias.
view is considered a virtual table because it acts like a table, and the same operations that can be performed on a table can be performed on a view.
But the virtual table doesn’t stay in the database. It gets created when we use the view and then deleted. The named VIEW is the only thing that persists. This is good, because each time new rows are inserted into the database, when you use a view it will see the new information.
view 对database的好处
-
You can keep changes to your database structure from breaking applications that depend on your tables. 例如使用python搜索database中的信息,我们可以使用view 创建的virtual table,而不是使用real table。这样,real table发生变化,如果不影响view,那么我们的python code就不需要改动。
-
Views make your life easier by simplifying your complex query into a simple command. 不需要重复写query,更容易,不易出错。
-
You can create views that hide information that isn’t needed by the user. 给定某些人的权限只是view,而不是real table,这样可以把real table中的sensitive info 过滤掉。
Join mutiple tables
可以使用join 连接多个table
CREATE VIEW job_raises AS
SELECT mc.first_name, mc.last_name, mc.email, mc.phone, jc.contact_id, jc.salary, jd.salary_low, jd.salary_low – jc.salary AS raise
FROM job_current jc
INNER JOIN job_desired jd
INNER JOIN my_contacts mc
WHERE jc.contact_id = jd.contact_id
AND jc.contact_id = mc.contact_id;
CHECK OPTION
CHECK OPTION added to your view tells the RDBMS to check each statement you try to INSERT and DELETE to see if it’s allowed according to the WHERE clause in your view.
CREATE VIEW pb_dimes AS
SELECT * FROM piggy_bank WHERE coin = 'D' WITH CHECK OPTION;
WITH CHECK OPTION: That makes the data entered into a view be verified against the WHERE clause before being allowed to be added.在此例句中输入的 coin 必须使‘D’。如果不是,则会报错。
使用view可以对real table进行UPDATE,INSERT INTO,DELETE等可以用于real table的操作。
updatable view
我们上面看到的view 都是updatable view。 An updatable view is a view that allows you to change the underlying tables.An updatable view includes all the NOT NULL columns from the tables it references.
A non-updatable view is a view that doesn’t include all the NOT NULL columns. Other than creating and dropping it, the only thing you can do with a non-updatable view is SELECT from it.
DROP VIEW view_name;
使用DROP VIEW pb_dimes;来删除view pd_dimes。可以使用DESC来查看VIEW中的column信息。
transaction
A transaction is a set of SQL statements that accomplish a single unit of work.

During a transaction, if all the steps can’t be completed without interference, none of them should be completed.
在一个交易中,如果遇到了干扰,不能完成,则交易中的所有内容都不会执行。
ACID test
acronym ACID: There are four characteristics that have to be true before we can call a set of SQL statements a transaction:
首字母缩写ACID,判断 a set of SQL statements是否是一个transaction。需要考虑以下四个特征:
-
ATOMICITY: 原子性。All of the pieces of the transaction must be completed, or none of them will be completed. You can’t execute part of a transaction. Mrs. Humphries’ samoleons were blinked into non-existence by the power outage because only part of the transaction took place. 在一个transaction 中的statement,要么全部执行完成,要么一个都不执行。
-
CONSISTENCY:一致性。A complete transaction leaves the database in a consistent state at the end of the transaction. At the end of both of the samoleon transactions, the money is in balance again. In the first case it’s been transferred to savings; in the second it’s been translated into cash. But no samoleons go missing. 相当于守恒定律。不会无缘无故的消失。
-
ISOLATION:隔离性。Isolation means that every transaction has a consistent view of the database regardless of other transactions taking place at the same time. This is what went wrong with John and Mary: Mary’s ATM could see the balance while John’s ATM was completing the transaction. She shouldn’t have been able to see the balance, or should have seen some sort of “transaction in progress” message. 即当前正在进行的transaction具有连续性,即其他的transaction不能影响其进行。
-
DURABILITY:持续性。After the transaction, the database needs to save the data correctly and protect it from power outages or other threats. This is generally handled through records of transactions saved to a different location than the main database. If a record of Mrs. Humphries’ transaction had been kept somewhere, then she might have gotten her 1,000 samoleons back. 可以应对突发情况,比如把transaction执行的过程记录在其他的地方,以防不测。
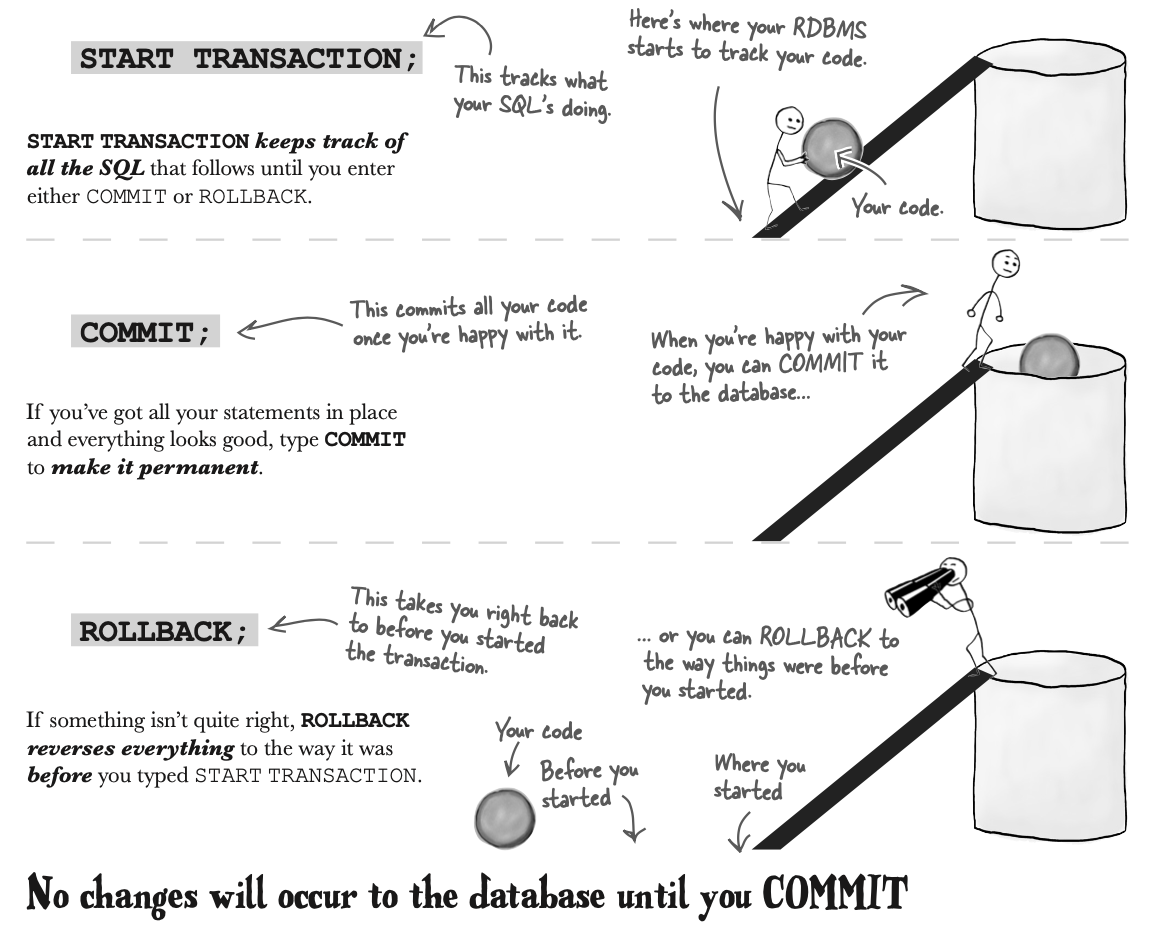
SQL transaction tools
START TRANSACTION;
COMMIT;
ROLLBACK;
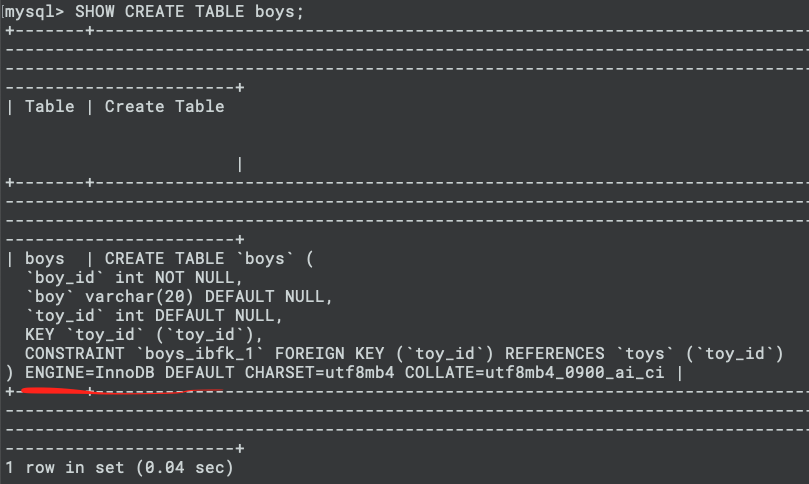
storage engine
You need to make sure your storage engine is either BDB or InnoDB, the two choices that support transactions. Engine 的信息,我们可以通过SHOW CREATE TABLE table_name来查看,如下:
To change your engine, use this syntax:
ALTER TABLE your_table ENGINE = InnoDB;
Do transaction
- ROLLBACK
START TRANSACTION;
SELECT * FROM piggy_bank; # see the original table content
UPDATE piggy_bank set coin = 'Q' WHERE coin = 'P'; # update the table
SELECT * FROM piggy_bank; # see the changes
ROLLBACK; # changed our minds, redo it
SELECT * FROM piggy_bank; # see whether the table is as the same as original
- COMMIT
START TRANSACTION;
SELECT * FROM piggy_bank; # see the original table content
UPDATE piggy_bank set coin = 'Q' WHERE coin = 'P'; # update the table
SELECT * FROM piggy_bank; # see the changes
COMMIT; # Make the change stick
SELECT * FROM piggy_bank; # see whether the table is as the same as original
想使用ROLLBACK 和 COMMIT,在之前应该先使用START TRANSACTION。因为只有这样RDBMS知道是从哪里开始的,以及rollback 到哪里。
因此使用START TRANSACTION 可以查看我们对于表格的更改是否满意,不满意就ROLLBACK,满意就COMMIT。这是一个不错的方法。不过应该及时进行ROLLBACK和COMMIT,因为RDBMS会产生一个transaction log,随着query statement增多,这个log 会增大,会浪费空间和计算机的资源去track the log.
security part2
有时我们需要为不同的员工设置不同的数据库操作权限,例如有的员工只能使用SELECT 功能,不能使用DROP,UPDATE,INSERT,DELETE等修改table的功能。
root user
root user可以具有任何操作,且可以设置新的用户,并为其设置权限。因此其密码应该保护,收到重视。 为root user 设置密码如下:
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = 'mypass';
# 如果没有 FOR user,那么就是修改当前user root
SET PASSWORD = 'auth_string';
Create new user
In MySQL, the statement to create a new user is as bellow:
CREATE USER elisa IDENTIFIED BY 'password123'
elisa: new user name
Decide exactly what the user needs
You can control exactly what users can do to tables and columns with the GRANT statement.
对不同的用户赋予不同的table 权限。同时也可以对不同的table赋予不同的权限,例如查看某些columns。
The GRANT statement can be used to give specific rights to users of our databases. Here’s what the GRANT can allow us to do:
- Only some users may modify particular tables.
- The data in a specific table may only be accessible to certain users.
- Even within tables there might need to be permissions: some users can see certain columns, but not others.
Set password for other users
-
首先进入到root账户:
mysql -u root -p -
然后修改user password
ALTER USER 'userName'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'New-Password-Here';
- Finally type SQL command to reload the grant tables in the mysql database:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
check current user
SELECT USER();
GRAND 用法
GRANT SELECT ON clown_info TO elsie;
SELECT: 要赋予的权限,select; clown_info: table name; elsie: user name
如果需要赋予多个表格的权限,则需要分开写。
GRANT SELECT ON activities TO elsie;
GRANT SELECT ON location TO elsie;
GRANT SELECT ON info_activities TO elsie;
GRANT SELECT ON info_location TO elsie;
GRANT variations
GRANT DELETE ON chores TO happy, sleepy; # 赋予多个user
GRANT INSERT,DELETE,UPDATE ON boys TO zeng; # 赋予多个权限
GRANT SELECT(chore_name) ON chores TO dopey; # 只能SELECT 特定的column
GRANT DELETE ON chores TO happy, sleepy WITH GRANT OPTION; # 赋予happy,sleeepy 在chores表格上的 DELETE 功能。并且由于有GRANT OPTION,他们也可以把此DELETE功能赋予给其他人。
GRANT ALL ON talking_animals TO bashful; # Allows bashful to SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT and DELETE on the talking_animals table.
GRANT SELECT ON woodland_cottage.* TO doc; # 赋予doc在woodland_cottage Databse 中的所有表格中有select 的工功能。
- You can name multiple users in the same GRANT statement. Each of the users named will get the same permission granted to them.
- WITH GRANT OPTION gives users permission to give other users the permission they were just given.It sounds confusing, but it simply means that if the user was given a SELECT on chores, he can give any other user that same permission to do SELECTs on chores.
- A specific column, or columns, in a table can be used instead of the entire table.The permission can be given to only SELECT from a single column. The only output the user will see will be from that column.
- You can specify more than one permission on a table. Just list each permission you want to grant on a table using a comma after each.
- GRANT ALL gives users permission to SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE from the specified table.It’s simply a shorthand way of saying “give users permission to SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE from the specified table.”
- You can specify every table in a database with security database_name.* Much like you use the * wildcard in a SELECT statement, this specifies all the tables in a database.
REVOKE privileges
收回赋予user的权限。REVOKE与GRANT用法很接近。不同之处是把GRANT换成REVOKE,把TO 换成FROM。如下:
REVOKE SELECT ON clown_info FROM elsie;
revoke the WITH GRANT OPTION but leave the privilege intact.
REVOKE DELETE, GRANT OPTION ON chores FROM happy, sleepy;
REVOKE privileges,GRANT OPTION ON table FROM user,参考stack overflow. happy and sleepy can not give the delete privilege to others now, but they still have the delete privilege themself.
在上面的revoke中,如果从sleep和happy收回DELETE,那么happy 和sleepy赋予其他user delete的权限也会一并收回。
REVOKING with precision
精确控制REVOK回收Privilege的程度.以下内容在MySQL中并不适用,参考网页内容
- CASCADE。
CASCADE, removes the privilege from the user you target (in this case, sleepy) as well as anyone else that that user gave permissions to.
REVOKE DELETE ON chores FROM sleepy CASCADE;
- RESTRICT
Using RESTRICT when you want to remove a privilege from a user will return an error if that user has granted privileges to anyone else.
REVOKE DELETE ON chores FROM sleepy RESTRICT;
GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO elsie;
赋予elsie全部数据库中的全部table SELECT 功能。The first asterisk refers to all database, the second to all tables.
roles
You need a way to give the groups the privileges they need, while at the same time giving each user an individual account.
A role is a way you can group together specific privileges, and apply those to everyone in a group.Your role becomes an object in your database that you can change as needed when your database changes, without having to explicitly change every single user’s privileges to reflect the database changes. 也就是说同一个role中的user会随着role中的previlege的变化而变化。当database发生变化时,只需要更改role的previlege即可。
- 创建role
CREATE ROLE data_entry;
data_entry: role name
- add privileges to the role
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON some_table TO data_entry;
data_entry: 在这里可以被当做一个user。
- 把role赋予其他user
GRANT data_entry TO doc;
data_entry: The role name takes the place of the table name and privileges.
- 回收user role 的权限
REVOKE data_entry FROM doc;
- drop role
DROP ROLE data_entry;
Using your role WITH ADMIN OPTION
Just like the GRANT statement has WITH GRANT OPTION, a role has the similar WITH ADMIN OPTION.
GRANT data_entry TO doc WITH ADMIN OPTION;
WITH ADMIN OPTION allows user doc to grant the role of data_entry to anyone else.
REVOKE with CASCADE and RESTRICT
REVOKE data_entry FROM doc CASCADE;
REVOKE data_entry FROM doc RESTRICT; # This will cause an error when doc give some the data_entry privilege.
Combining CREATE USER and GRANT
同时创建和赋予权限
GRANT SELECT ON clown_info
TO elsie
IDENTIFIED BY 'cl3v3rp4s5w0rd';
Because the user elsie has to be created before she can have privileges granted to her, your RDBMS checks to see if she exists, and if not, it automatically creates her account.
APPENDIX
ALL, ANY, and SOME
以上三个关键词可以用在subquery 之前。如下:
SELECT name, rating FROM restaurant_ratings
WHERE rating > ALL
(SELECT rating FROM restaurant_ratings WHERE rating > 3 AND rating < 9);
ALL : 表示返回的结果,rating要比subquery中的最大的那个还要大。
SELECT name, rating FROM restaurant_ratings
WHERE rating > ANY
(SELECT rating FROM restaurant_ratings WHERE rating > 3 AND rating < 9);
ANY: rating 比其中的任何一个大就行。 SOME 和ANY的用法一致,需要查看相关RDBMS资料。
Data types
-
BOOLEAN: The boolean type allows you to store ‘true’, ‘false’, or it can be left NULL. Behind the scenes, your RDBMS is storing a 1 for true values, and a 0 for false values. You can insert 1 or ‘true’, 0 or ‘false’.
-
DATE_FORMAT:
修改返回的时间类型。例如:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(a_date, '%M %Y') FROM some_dates;
output : August 2007,January 1925
Create a temporary table
创建临时table的目的有:
- 只是临时需要储存数据,例如各种数学计算得出的结果
- 抓取table中的某些列
- 在使用programming language操作时,现生成临时的,最后再储存到其他table中。
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE my_temp_table (
some_id INT,
some_data VARCHAR(50) )
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE my_temp_table AS
SELECT * FROM my_permanent_table;
CAST data types
CAST(your_column, TYPE)
TEMPORARY : 只需要添加这个关键词即可,与正常创建table一致。