Table of contents
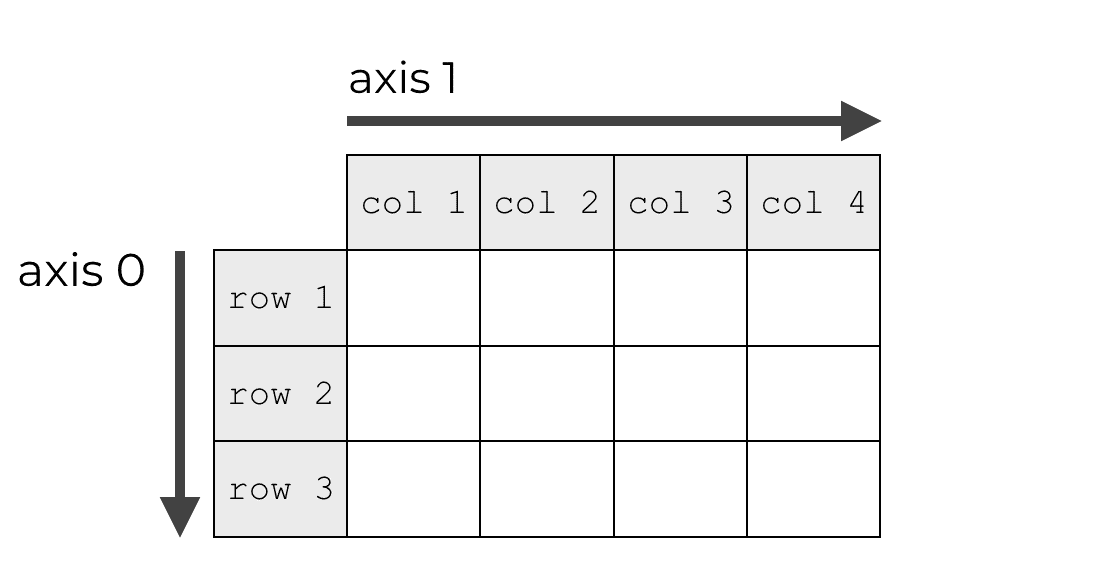
numpy axis
这篇文章 对numpy 的 axis解释的不错。直观的看下图:
numpy.array_equal
判断两个numpy array是否相同。只返回一个bool value, True or False。而不是一个bool matrix。
numpy.argmax(a, axis=None, out=None)
Returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis. 返回指定axis最大值的indices.如果是二维matrix,我们想求每一行中的最大值的indice,我们可以这样写indexs = np.argmax(circle_matrix,axis=1)
numpy.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None)
可以用于对weights的初始化。
Parameters:
- loc : mean
- scale : std
- size : number of data
[numpy.ravel(a, order=’C’)]
Return a contiguous flattened array.
x = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
np.ravel(x)
# output : array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
numpy.dot(a, b, out=None)
两个matrix进行相乘。
- 如果a,b 是一维的数组,则是进行点乘。
- 如果a,b 是多维数组,则推荐使用
matmul or a @. here @ calls np.matmul . 这是因为在处理大的matrix时,后两者的处理速度要比numpy.dot 更快。参考stack overflow
numpy.matmul
多维数组进行相乘。不能是scaler value。
shape that matches the signature (n,k),(k,m)->(n,m).
np.vstack OR np.hstack
X_combined_std = np.vstack((X_train_std,X_test_std))
y_combined = np.hstack((y_train,y_test))
- np.vstack : 一行一行的叠加, vertically (row wise)
- np.hstack : 一列一列的叠加, horizontally (column wise).
numpy.where
numpy.where(condition[, x, y])
如果condition 返回True,则返回x,otherwise,return y.
a = np.arange(10)
np.where(a < 5, a, 10*a)
np.argsort(a)
Returns the indices that would sort an array.对array a 进行从小到大排序。
a = np.array([0,2,1,4,3,5])
indices = np.argsort(a)[::-1] # 从大到小进行排序
numpy.cumsum(array)
Return the cumulative sum of the elements along a given axis.相当于前缀和
numpy.linspace
numpy.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None, axis=0)
把从start 和stop中间的距离进行分割成num份